Understanding the mental health crisis among Japanese adolescents
As suicide has become the leading cause of death among young people aged 15 to 34 in Japan, adolescent mental health has become a pressing concern. An in-depth six-year study by the University of Tokyo and the Tokyo Metropolitan Institute of Medical Sciences has shed light on this critical issue, revealing hidden mental health issues among Japanese adolescents. The study, which surveyed 2,344 adolescents and their caregivers, aimed to better understand the factors affecting adolescent mental health.
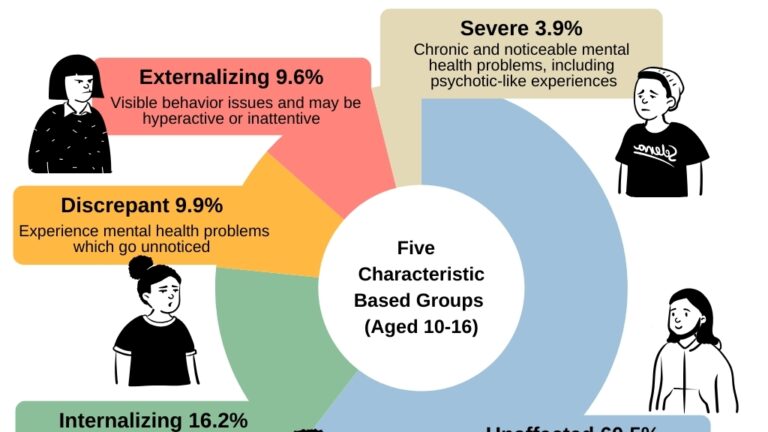
The researchers used deep learning techniques to identify five distinct categories of adolescents based on the trajectory of their symptoms, including unaffected, internalizing, divergent, externalizing, and severe. Alarmingly, nearly 40% of the teens surveyed were experiencing some issues, and nearly 10% of them were living with mental health issues that had not been identified by their caregivers. This subgroup had the highest risk of self-harm and suicidal thoughts, highlighting the urgent need for early intervention and preventative strategies.
The impact of social media and academic pressure
The study also explored the influence of social media and academic stress on adolescent mental health. High academic pressure and excessive use of social media were linked to higher levels of anxiety and depression among adolescents. In fact, students who spent more than three hours a day on social media were more likely to suffer from mental health problems. These findings highlight the importance of providing support and resources to adolescents to manage academic stress and social media pressures.
The role of caregivers in adolescent mental health
Interestingly, the study also highlighted the significant impact of caregivers’ mental state on adolescents’ mental health. The mental state of caregivers has been found to influence the mental health trajectory of their services, further complicating the already complex picture of adolescent mental health. This highlights the importance of societal involvement and support not only from adolescents, but also from their caregivers, in managing mental health problems.
Facing the mental health crisis
The study’s findings provide a clear call to action. As suicide rates among youth and children in Japan reach record levels since 1978, the need for prevention efforts and early intervention strategies has never been more urgent. It is crucial to provide support to adolescents facing mental health issues and recognize signs of mental health problems that might otherwise go unnoticed. The study also highlights the importance of societal involvement in recognizing and supporting adolescents facing difficulties, as well as their caregivers.
The results of this study not only highlight the multifaceted nature of adolescent mental health problems, but also highlight the urgency of implementing preventive measures and early interventions. As we work to combat the increase in youth suicide and promote the overall well-being of adolescents, it is essential to consider the diverse and dynamic nature of adolescent psychopathology as well as the crucial role of caregivers and of society as a whole.